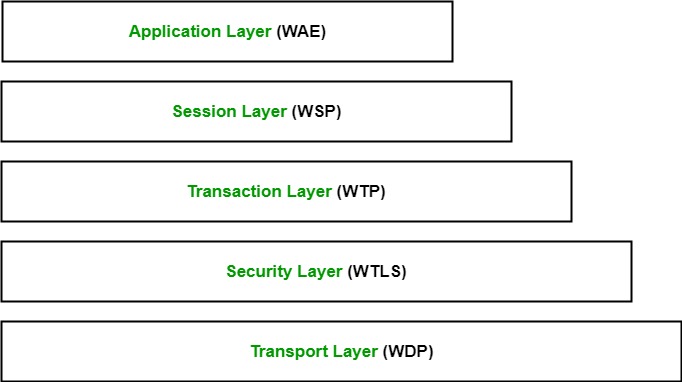
The Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a set of communication protocols and an application programming model based on the World Wide Web (WWW). Its hierarchical structure is quite similar to the TCP/IP protocol stack design.
WAP stands for Wireless Application Protocol. It is a protocol designed for micro-browsers and it enables access to the internet in mobile devices. It uses the markup language WML (Wireless Markup Language and not HTML), WML is defined as an XML 1.0 application. It enables the creation of web applications for mobile devices. In 1998,
WAP Forum was founded by Ericson, Motorola, Nokia and Unwired Planet whose aim was to standardize the various wireless technologies via protocols. WAP protocol resulted from the joint efforts of the various members of WAP Forum. In 2002, WAP forum was merged with various other forums in the industry resulting in the formation of
Open Mobile Alliance (OMA)

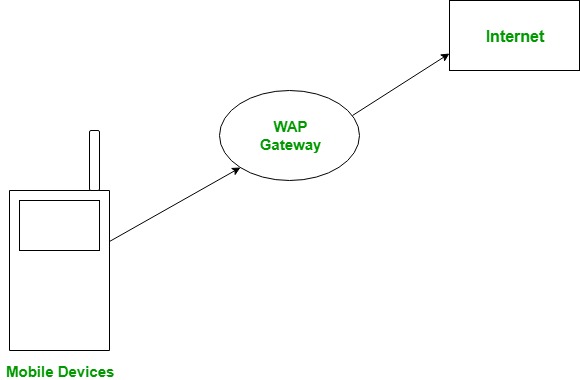
The user opens the mini-browser in a mobile device. He selects a website that he wants to view. The mobile device sends the URL encoded request via network to a WAP gateway using WAP protocol.
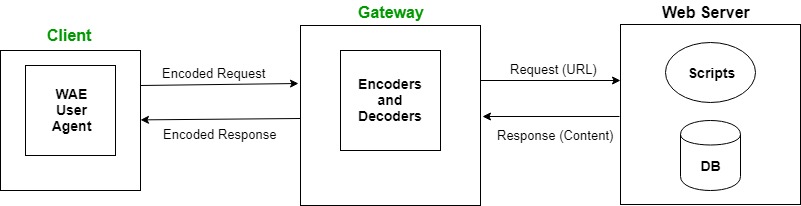
The WAP gateway translates this WAP request into a conventional HTTP URL request and sends it over the internet. The request reaches to a specified web server and it processes the request just as it would have processed any other request and sends the response back to the mobile device through WAP gateway in WML file which can be seen in the micro-browser.
The following advantages for wireless network operators, content producers, and end users were put out by WAP when it was first introduced in 1999:
Operators of wireless networks and mobile phones: WAP was created with the intention of enhancing already-existing wireless data services, such as voicemail, and facilitating the creation of new mobile applications. Without making any further infrastructure adjustments or phone modifications, these applications might be created.
Content Provider: For third-party application developers, WAP opened up a market for extra applications and mobile phone features. It was suggested that developers use the WML programming language to write applications for mobile devices.
End users: Access to online services like banking, entertainment, messaging, and other information on mobile devices should be simple and safe for users of mobile phones. WAP could also permit access.
The benefits of Wireless Application Protocol, or WAP, are listed below:
The following is a list of various Wireless Application Protocol, or WAP, drawbacks:
Internet access was only accessible from your computer until the release of the first WAP devices. With WAP, you may now use your mobile phone to use the Internet to interact with other people. large global communication and data sharing are therefore expanded.
There is a WAP browser available as well, just like your personal internet browser. Micro WAP Browser is the name of the browser used to access websites using a WAP device. What makes it unique is that it uses less hardware, memory, and CPU resources and presents the data in WML, a constrained mark-up language.
WAP 2.0, which was introduced in 2002, is only a combination of end-to-end HTTP and XHTML. The gateway and custom protocol suite that were used to communicate with have been removed.